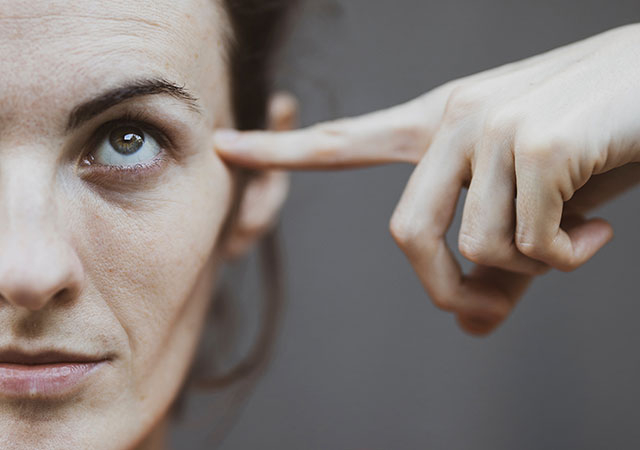
What is the Brain?
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body. It controls your every movement, sensation, thought, word and emotion. In other words, it controls what you do and determines who you are. The brain weighs about 1.3 kilograms (3 pounds) and has several thousand miles of interconnected nerve cells; all fed by a system of tiny blood vessels. These blood vessels bring oxygen and energy in the form of nutrients to the brain. Even though the brain amounts to only 2% of body weight, it consumes 20% of your oxygen and energy supply.
Ruth Wilcock, CEO for OBIA
(Ontario Brain Injury Association)
What is the Brain?
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body. It controls your every movement, sensation, thought, word and emotion. In other words, it controls what you do and determines who you are. The brain weighs about 1.3 kilograms (3 pounds) and has several thousand miles of interconnected nerve cells; all fed by a system of tiny blood vessels. These blood vessels bring oxygen and energy in the form of nutrients to the brain. Even though the brain amounts to only 2% of body weight, it consumes 20% of your oxygen and energy supply.
Hover over the Brain Regions to See
More Information
What is Acquired Brain Injury?
Acquired brain injury is
any damage to the brain that occurs after birth and is not related to a congenital disorder, a developmental disability, or a process which progressively damages the brain.
VS.
Acquired brain injury
is Not
Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, or Parkinson’s disease.
Traumatic brain injury
occurs when damage to the brain is caused by an external blow or shake.
VS.
Non-traumatic
brain injury
is damage to the brain caused by disease or oxygen deprivation.
Types of Acquired Brain Injury
Traumatic Brain Injury
o Falls
o Motor vehicle collisions
o Assaults/blow to the head
o Severe shaking
(i.e. intimate partner violence or shaken baby syndrome)
Non-Traumatic Brain Injury
o Infections (i.e. meningitis, encephalitis, etc.)
o Stroke
o Aneurysm
o Anoxia (ie. strangulation, near-drowning, overdose)
o Inhaling or ingesting toxins
Traumatic Brain Injury
o Falls
o Motor vehicle collisions
o Assaults/blow to the head
o Severe shaking
(i.e. intimate partner violence or shaken baby syndrome)
Non-Traumatic Brain Injury
o Infections (i.e. meningitis, encephalitis, etc.)
o Stroke
o Aneurysm
o Anoxia (ie. strangulation, near-drowning, overdose)
o Inhaling or ingesting toxins
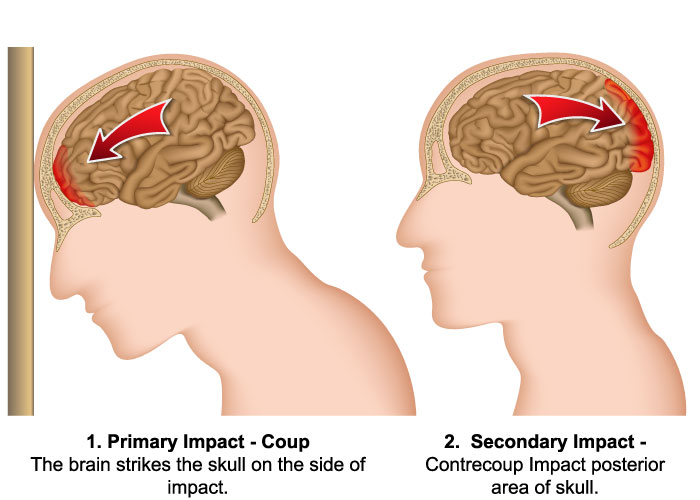
What happens when the
brain is injured?
The brain is extremely fragile. When a group of neurons are damaged, they die and the neurons they used to communicate with will no longer receive information. Once these neurons are no longer receiving information from the damaged neurons, they become inactive and consequently die. This process is called the cascade effect and is how an injury to one part of the brain results in damage to surrounding areas. This is why treatment and rehabilitation are critical at specific stages of recovery.
Facts and Fiction about Brain Injury
Click the plus (+) sign below to expand
FACT
No two brain injuries are alike. The brain is a very complex organ, and brain injury is not like any other disease or injury. The degree of recovery from ABI depends on the severity of the injury and the part of the brain involved. Other determinants to the severity of the brain injury include a decreased supply of oxygen, blood clots, tearing and shearing forces on the neurons, as well as swelling and bruising in the brain.
FICTION
Brain injuries heal with time.
FACT
Once a neuron’s nucleus (cell body) is damaged the neuron dies and a new one does not regenerate. Although this damage is permanent, through a process called neuroplasticity, other neural pathways can reorganize themselves to help compensate for the damage.
FICTION
All brain injuries are the same.
FACT
Some individuals with a severe brain injury show no outward physical signs of impairment. Cognitive abilities (e.g. memory, abstract thinking, attention, and judgement) can be seriously or permanently affected even in the absence of physical injuries.
FICTION
A good physical recovery indicates that the brain has healed completely.
FACT
Even though a child’s brain has more plasticity and greater potential ability for other neurons to take on new function, overall the brain is less developed. Children have a smaller backlog of pre-existing knowledge (including life experience and skills) to help them adjust to the consequences of ABI.
FICTION
Given similar injuries, children will have better outcomes than young adults.